- VMware
- VMware vCenter Server (VCSA), VMware vSphere
- 28 February 2025 at 12:26 UTC
-

- 1/8
In business, it is essential to ensure the high availability of your various services and applications to avoid service interruptions.
For this, you will find many features in VMware vSphere, part of which is necessary for enabling VMware HA.
In addition, you will also see that another VMware product will also allow you to improve it to achieve the best possible level of service for your VMware virtual infrastructure.
- What is high availability (HA)?
- Make a fully available VMware vSphere infrastructure
- What is VMware vSphere HA (High Availability)?
- VMware vSphere HA prerequisites and best practices
- iSCSI datastores accessible by cluster hosts
- Check VMware vSphere HA prerequisites
- Ensure uplink redundancy for the management network
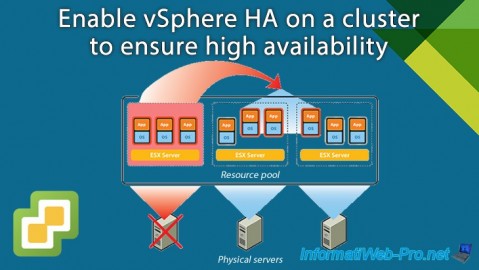
- Enable VMware vSphere HA on your cluster
- VM overrides
- Testing vSphere HA (failed host)
- Testing vSphere HA (isolated host - no HA response configured)
- Testing vSphere HA (isolated host - with HA response configured)
1. What is high availability (HA)?
A highly available system is one that is continuously operational for a long period of time.
A fault-tolerant system is designed so that a backup component immediately takes over in the event of a failure so that there is no interruption of service.

To do this, you can use features available under VMware vSphere, as well as the VMware vCenter Site Recovery Manager (also called SRM) product.
Source : VMware vSphere 4.1: Install, Configure, Manage – Revision A - High Availability Module 12 - VMware (pages 7 and 8).
2. Make a fully available VMware vSphere infrastructure
To make a VMware vSphere infrastructure fully highly available, you will need to manage high availability at different levels: hardware protection, zero downtime, and protection against unplanned downtime and disasters.
To do this, you will need to ensure the high availability of:
- Components: NIC Teaming, redundant switches, multipathing, RAID controller, redundant power supply, ...
- Server: VMware vSphere features. Such as vSphere vMotion (VM migration), vSphere DRS (automatic VM migration), vSphere HA (high availability) and vSphere Fault Tolerance.
- Storage: vSphere Storage vMotion feature (VM storage migration).
- Data: use third-party backup software, such as "Veeam Backup & Replication".
- Site: the VMware Site Recovery Manager product allows you to create and maintain a backup environment (a second site) in real time so that it can automatically take over without interruption if the main environment (production environment) fails .
Note: on the left, this corresponds to the 99% service level and the further you go to the right, the more you arrive at the 99.999% service level. That said, the further right you go, the more technical skills and money it requires to best ensure the high availability of your VMware hardware and virtual infrastructure.

In addition to high availability for your VMware servers, don't forget to add high availability for related services:
- storage servers: NFS, iSCSI with MPIO, ...
- Active Directory (AD) infrastructure with at least 2 domain controllers per Active Directory domain.
- If you are using the Windows Server (deprecated) version of vCenter Server, also implement SQL Server high availability.
- if you are using VCSA appliance, then VMware HA will be sufficient for vCenter Server.
Source : VMware - Delivering Business Continuity Solutions with VMware Virtualization (page 7)
3. What is VMware vSphere HA (High Availability)?
VMware vSphere HA provides a simple way to ensure high availability of your applications.
In the event of a VMware ESXi host failure, the affected virtual machines will be automatically restarted on other VMware ESXi hosts.
VMware vSphere HA therefore makes it possible to reduce downtime for your services without having to resort to additional hardware and/or software.
In the background, VMware vSphere HA monitors all VMware ESXi hosts in a resource pool for possible failures of one or more hosts.
To do this, an agent called FDM (Fault Domain Manager) is automatically added to each host to ensure a heartbeat signal between them.
Thus, in the event of loss of the heartbeat signal, the virtual machines on the failed host are restarted on the other hosts in the resource pool.
Notes :
- VMware vSphere HA continuously monitors resource usage so that virtual machines can be restarted on other hosts in case one host fails.
- Forced restart of VMs currently owned by a failed host is possible thanks to the VMFS file system which is designed to handle simultaneous access by multiple servers.

Source : VMware High Availability - Cost effective high availability for virtual machines.
When you enable VMware vSphere HA on a VMware cluster, an FDM agent is added automatically on each VMware ESXi host.
Note that the "hostd" is already present as standard on your VMware ESXi hosts, because it is it which manages many of the basic actions of your hypervisor. In addition, this FDM agent communicates directly with the "hostd". So it cannot work without the "hostd".
When you enable VMware vSphere HA, one of the hosts is automatically designated as the Master host. This main host is the one that will communicate with vCenter and monitor the other hosts, as well as their VMs.
Since different types of failures can occur, the primary host will use the network heartbeat signal, as well as the heartbeat signal from the datastore, to know what type of failure it is.
Other hosts will be designated as secondary hosts (Slaves).
Note that similar to a vDS switch, vCenter Server is only needed to configure VMware vSphere HA.
Indeed, VMware vSphere HA can continue to function correctly even if vCenter Server is inaccessible, because a copy of the configuration is present on each cluster member host (where VMware vSphere HA is enabled).
Source : How vSphere HA Works - VMware Docs.

4. VMware vSphere HA prerequisites and best practices
To use VMware vSphere HA, you must:
- have a VMware cluster.
- have at least 2 VMware ESXi hosts: to be able to restart the VMs of a host that fails on another functional host in the cluster.
- have a cluster with hosts that preferably have an identical processor model.
Otherwise, enable EVC mode so that the VMs can be live migrated to any host in the cluster where VMware HA will be enabled. - have at least one management network (which is normally already the case and which by default corresponds to the "Management Network").
Indeed, it is via the management network that VMware HA communication will pass. - have a management network at least in Gigabit Ethernet so that the VMs can be migrated via vMotion.
This is a vMotion prerequisite. But VMware HA will migrate VMs between your hosts using this feature. - have shared storage (e.g. iSCSI or NFS) accessible by all hosts in your VMware cluster so that a VM from a faulty host can be restarted from any host in the VMware cluster.
- virtual machines, along with their configuration files, must be on this shared storage.
When you want to use VMware vSphere HA, VMware recommends that you:
- implement network path redundancy: use at least 2 physical network cards for the management network of your VMware ESXi hosts.
For that :- add at least a 2nd physical network adapter to the virtual switch corresponding to your hosts management network.
- connect this 2nd physical network adapter, preferably, to a second physical switch.
To benefit from fault tolerance regarding the physical switch. - assign this new physical network adapter to the virtual network serving as the management network as an active adapter or standby adapter.
- change the load balancing type to: Route based on originating port ID (which corresponds to the "Route based on originating virtual port" value under vCenter Server).
- disable failback.
- use at least 2 datastores (shared storage) to ensure redundancy of the heartbeat signal. Otherwise, a warning will be displayed on your hosts once VMware HA is enabled.
Additionally, VMware recommends using datastores located on at least 2 different iSCSI or NFS servers (although this is optional).
Warning: you cannot use a vSAN datastore for VMware HA heartbeat. - use VMware ESXi hosts with a fixed, non-dynamic IP address.
Indeed, high availability uses DNS resolution. This could be a problem if hosts have IP addresses dynamically assigned via a DHCP server.
Sources :
- Create a vSphere HA Cluster in the vSphere Client - VMware Docs
- Best Practices for VMware vSphere® High Availability Clusters - Best Practices for Networking - VMware Docs
- Networking Best Practices for vSphere vMotion - VMware Docs
- Configure Heartbeat Datastores - VMware Docs
- Datastore Heartbeating - VMware Docs
5. iSCSI datastores accessible by cluster hosts
On one of the hosts, add your iSCSI server(s) in the "Dynamic Discovery" tab.
As stated before, you will need at least 2 datastores for the heartbeat signal. Additionally, VMware recommends creating these on different iSCSI servers (although you can also create them on a single iSCSI server).
In our case, we installed 2 iSCSI servers on Windows Server and added them to the software iSCSI controller of our host "esxi1".
To learn how to configure this software iSCSI controller on VMware vSphere, refer to our tutorial: VMware vSphere 6.7 - Create an iSCSI datastore.

From this host, create a VMFS datastore on each device (iSCSI disk).
In our case, we created a datastore "iSCSI DS 1" on the 1st disk (which is on our 1st iSCSI server) and a datastore "iSCSI DS 2" on the 2nd disk (which is on our 2nd iSCSI server).

By going to the "Storage -> Storage Devices" section, you can see where each iSCSI disk is located via the "Paths" tab.
As you can see, our datastore "iSCSI DS 1" is located on an iSCSI disk of our iSCSI server "iscsi1".

For our "iSCSI DS 2" datastore, this is located on an iSCSI disk of our iSCSI server "iscsi2".

Once the iSCSI datastores are created from your 1st host, add the iSCSI targets (iSCSI servers) to the software iSCSI controller of the other hosts in your cluster (where you will enable vSphere HA later).

Your other hosts will see the same iSCSI disks and the datastores created on them.
If not, click "Rescan Storage" to have VMware vSphere detect the datastores there.

As expected, in the list of storage devices on your other hosts, you will see that one datastore is on one iSCSI server and the other datastore is on another iSCSI server.


Share this tutorial
To see also
-

VMware 4/24/2024
VMware vSphere 6.7 - Extend a datastore (on a second hard drive)
-
VMware 8/14/2024
VMware vSphere 6.7 - Generate graphics with SexiGraf
-
VMware 11/27/2024
VMware vSphere 6.7 - Migrate VMs via vMotion (accross datacenters)
-
VMware 4/26/2024
VMware vSphere 6.7 - SIOC (Storage I/O Control)

You must be logged in to post a comment