- VMware
- VMware vCenter Server (VCSA), VMware vSphere
- 14 February 2025 at 15:40 UTC
-

- 1/2
In an enterprise with multiple VMware ESXi hosts, you will create a VMware cluster to benefit from high availability, fault tolerance, as well as better power available resources.
- What is a VMware vSphere cluster?
- Prerequisites and limitations of a VMware vSphere cluster
- Create a VMware vSphere cluster
- Add a host to the cluster
- Migrate the VCSA VM to your cluster
- Add another host to the cluster
- Create a virtual machine on your VMware vSphere cluster
1. What is a VMware vSphere cluster?
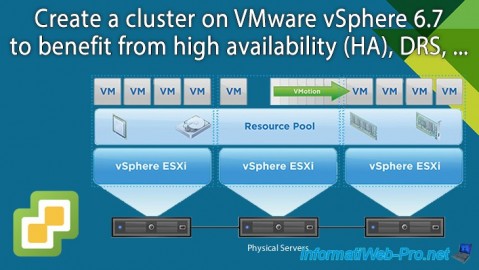
A VMware vSphere cluster is a set of VMware ESXi hosts that each have resources (CPU, RAM and storage), but which can be used as a single resource pool (as you can see in the VMware diagram below) .
Thanks to various VMware vSphere features, you will be able to benefit from:
- load distribution: if VMware vSphere DRS (Distributed Resource Scheduler) is activated, you will be able to create a virtual machine on your VMware vSphere cluster and the choice of the most suitable host at that precise moment will be made automatically.
DRS will also be able to dynamically migrate virtual machines from one host to another to improve resource utilization. - better performance: as said before, DRS can migrate virtual machines to improve resource utilization on your hosts.
But, it can also allow you to migrate a virtual machine to another host in your cluster if the current host is not able to provide it with the requested resources. - high availability: thanks to vSphere HA, your virtual machines can be restarted on another host in the cluster if the host where they are located fails.
Hence the importance of using shared storage (iSCSI, FC, ...). - reduced power consumption: thanks to VMware vSphere DPM (Distributed Power Management), a host can be released if possible so that it goes to sleep and therefore allow you to save electricity.
- Fault Tolerance: using VMware vSphere Fault Tolerance (FT), you can create a mirror VM that is synchronized from the primary VM and will take over in the event of a primary VM failure.
Failover will be managed automatically using vSphere DRS and vSphere HA. - vSAN: creating a cluster also allows you to activate the "VMware vSAN" option. Which allows you to create shared storage that will be managed via VMware vSAN.
However, this requires a VMware vSAN license in addition to your current VMware vSphere license.
Sources :
- Distributed Resource Scheduler | VMware vSphere
- What is Fault Tolerance and How it Works? | vSphere | VMware
- License Requirements - VMware Docs

2. Prerequisites and limitations of a VMware vSphere cluster
To create a VMware vSphere cluster, there are several prerequisites:
- You must have at least one data center in your VMware vSphere inventory.
Indeed, a cluster can only be created in a data center or a child folder of it. - VMware ESXi hosts must have the same version and update level.
- Preferably use VMware ESXi hosts with identical processors to benefit from better performance.
Although the use of different, but similar processors is possible thanks to EVC mode. But, at the expense of performance.
At a minimum, use processors from the same manufacturer (Intel/AMD). - preferably use shared storage (iSCSI, NAS, FC, ...) accessible by all the hosts in your cluster to be able to migrate the execution of a virtual machine from one host to another without having to migrate its storage.
This will reduce network bandwidth usage and speed up VM migrations. - vMotion must be enabled on at least one VMkernel interface on each host for migration of VMs from one host to another to be possible.
Sources of prerequisites:
- Create Clusters in the vSphere Client - VMware Docs
- Change the EVC Mode for a Cluster - VMware Docs
- vMotion Shared Storage Requirements - VMware Docs
Limits :
- each VMware ESXi 6.7 host can manage up to 1024 virtual machines.
- each cluster can manage up to 64 VMware ESXi hosts, 8000 virtual machines and 1600 resource pools.
Source of limits : vSphere 6.7 Configuration Limits.
3. Create a VMware vSphere cluster
To create a VMware vSphere cluster, select a datacenter in your inventory and click: Actions -> New Cluster.
Note: a cluster can only be created in a data center or a folder located there.

In the "New Cluster" wizard that appears, provide a name for your cluster and click OK.

The cluster has been created.

4. Add a host to the cluster
To add a host to your cluster, select your cluster and click: Actions -> Add Hosts.

The "Add Hosts" wizard appears.
In the "Existing Hosts" tab, select the host on which no virtual machines are powered on.
In our case, we first add our host "esxi2". Because our VM "VCSA" is currently powered on on our host "esxi1".
Note: as noted here, the host you add to a cluster will be put under maintenance. Which means that no virtual machines can be powered on while the host is added to the cluster.

A summary of the host to add to the cluster appears.
Click Next.

Click Finish.

The host has been added to your cluster.
In recent tasks, you will see the tasks appear in particular:
- Set the host to the desired state and move it to the cluster.
- Add a set of standalone hosts.

As you can see, the host added to your cluster has been automatically put into maintenance mode.

Click: Actions -> Maintenance Mode -> Exit Maintenance Mode.

Share this tutorial
To see also
-

VMware 3/3/2023
VMware ESXi 6.7 - Add a VMkernel interface
-

VMware 6/8/2022
VMware ESXi 7.0 / 6.7 - DCUI console presentation
-

VMware 3/6/2024
VMware vSphere 6.7 - Enable SSH protocol on VCSA
-

VMware 6/28/2024
VMware vSphere 6.7 - Tasks and events

You must be logged in to post a comment