Put a host or datastore in a cluster under maintenance on VMware vSphere 6.7
- VMware
- VMware vCenter Server (VCSA), VMware vSphere
- 14 March 2025 at 13:04 UTC
-

- 3/3
3. Monitor a cluster
While we're talking about cluster maintenance, here's how to maintain (or monitor) your cluster.
To begin, when you select your cluster, you can see a summary with the resources (CPU, memory and storage) used by your cluster.
In other words, it is the addition of the resources of all the hosts present in it.
You will also see icons corresponding to the different features that you can enable on your cluster.
In this case: vSphere DRS (automated VM migration), vSphere HA (high availability) and vSphere DPM (host power management).
In the "Cluster Consumers" section, you will be able to see the number of resource pools, vApps and virtual machines that are there.
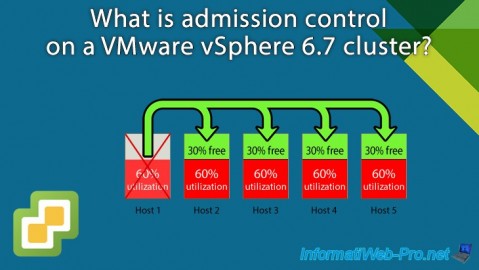
In the vSphere HA section, you will see information regarding failover capabilities that depend on the type of admission control used with vSphere HA.
You will also see which vSphere HA options are enabled, such as: Host and VM monitoring.

A little further down, you will find information regarding:
- Update Manager: update management.
- Cluster Resources: the number of hosts present in the cluster, as well as whether EVC (Enhanced vMotion Compatibility) mode is enabled.
- vSphere DRS: if this feature is enabled on your cluster, this will give you information regarding its vSphere DRS configuration.
For example: the number of recommendations made by DRS, the automation level chosen for vSphere DRS, ...

In the "Monitor" tab of your cluster, you will find a lot of information regarding:
- Issues and Alarms: issues and alarms that may have been triggered on your cluster.
- Performance: the performance of your cluster.
- Tasks and Events: tasks and events that occurred on your cluster.
Which is very useful in case of problems. - vSphere DRS: recommendations made by DRS, its history, resource usage (CPU, memory and network), ...
Note: this feature is not enabled by default. - vSphere HA: information regarding high availability, the name of the host designated as master, ...
Note: this feature is not enabled by default.

As you can see, it is possible to see the history of tasks performed on your cluster, its hosts and its virtual machines.

If vSphere DRS is enabled and it has made recommendations, you will see them in the "vSphere DRS -> Recommendations" section.

For high availability, you will be able to know:
- the host designated as master.
- the number of slave hosts connected to the master.
- the number of hosts that are in error or that are in an isolated or partitioned network (occurs when the heartbeat signal between hosts in the cluster is no longer exchanged due to a network problem).
- the number of virtual machines protected or not by vSphere HA
- the total resources of the cluster, as well as the resources reserved for failover.
- and more.

In "Resource Allocation -> CPU", you will see the CPU resources used by the virtual machines in your cluster, as well as what is currently reserved.

In "Resource Allocation -> Memory", you will see the RAM used by the virtual machines in your cluster, as well as what is currently reserved.

The same goes for storage.

Finally, in the "Usage" section, you can quickly monitor your cluster's consumption of CPU, memory and guest memory resources.
To understand the different terms used for guest memory, refer to our article: How memory (RAM) management works on VMware ESXi 6.7.

Share this tutorial
To see also
-

VMware 9/28/2022
VMware ESXi 6.7 - Join the hypervisor to an Active Directory domain
-

VMware 5/15/2024
VMware vSphere 6.7 - Add a physical disk to host
-
VMware 3/5/2025
VMware vSphere 6.7 - Cluster admission control
-
VMware 10/30/2024
VMware vSphere 6.7 - Secure access to VMware vCenter Server (VCSA) over HTTPS (via SSH)

No comment