- RAID
- 11 April 2025 at 10:59 UTC
-

- 1/2
When you create a single RAID logical drive on a single RAID array configured on your Microsemi Adaptec SmartRAID controller, it is easy to locate this drive from the Windows interface or from Linux.
In fact, it is enough to base it on the name of the logical disk seen by the operating system, or even its capacity (size).
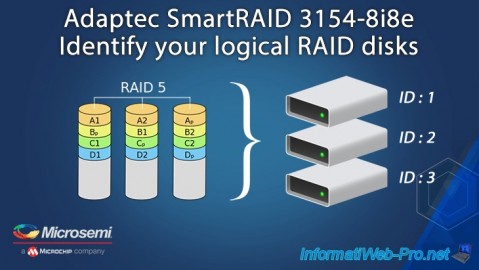
However, if you create several RAID logical disks on the same RAID controller and they have exactly the same capacity, you will need to find the correspondence between the disk identifier visible on your RAID controller and each logical disk seen by the operating system.
Here's how you can differentiate between your different RAID logical drives in Windows, as well as Linux and VMware ESXi (as an example).
- Find the ID of a RAID logical drive via ACU (Array Configuration Utility)
- Find the ID of a RAID logical drive via the web interface (maxView Storage Manager)
- Locate a RAID logical drive created on an Adaptec SmartRAID controller on Windows
- Locate a RAID logical drive via the Windows installer
- Locate a RAID logical drive via the VMware ESXi installer
- Locate a RAID logical drive in your VMware ESXi hypervisor storage
1. Find the ID of a RAID logical drive via ACU (Array Configuration Utility)
When you start your computer, information about your Microsemi Adaptec SmartRAID controller appears before your operating system (Windows, Linux, ...) starts.
Then, a message asking you to press "Ctrl + A" (with a QWERTY keyboard) or "Ctrl + Q" (with an AZERTY keyboard) appears.
Press these 2 keys simultaneously so that the message "Microsemi SAS/SATA Configuration Utility will be invoked after initialization" is displayed.
Once your Microsemi Adaptec SmartRAID controller has finished booting, the Configuration Tool (ACU) will appear.

In the configuration tool (ACU) that appears, go to: Array Configuration.

Then, go to: Manage Arrays.

Select your RAID array and press Enter to see the list of RAID logical drives created on it.

Select a RAID logical drive (recognizable here by its name) and press Enter to get more information about it.

The identifier visible on Linux is the one indicated in the "Drive Unique ID" line.
In our case: 600508b100...
Note: to find out which physical disks are used by this logical RAID disk, press the "Ctrl + D" keys (as shown at the bottom of the screen).

The list of physical disks on which this RAID logical disk depends appears.

2. Find the ID of a RAID logical drive via the web interface (maxView Storage Manager)
One of the big advantages of RAID controllers designed by Microchip (Microsemi) is that you can obtain a lot of information concerning your physical disks, your RAID arrays, your logical RAID disks, ... thanks to the "maxView Storage Manager" web interface.
To find the identifier of one of your RAID logical drives with a Microsemi Adaptec SmartRAID controller, access the "maxView Storage Manager" web interface and go to: localhost (127.0.0.1) -> Controller 1 -> Arrays and Logical Devices -> [name of your RAID array] -> [name of one of your RAID logical drives].
In the "Summary" tab, locate the "Volume Unique Identifier" information.
Again, we find the identifier "600508b100...".
As a reminder, this identifier is visible under Linux (and on other Linux-based operating systems).

In the "Resources" tab, you can also very easily see:
- Physical Device(s): the list of physical disks used by this RAID logical disk.
- Disk Partition Information: the partition table currently present on this RAID logical disk.

In the "Summary" tab, you will also find the name of this disk (Disk Name) visible by the current operating system.
On Windows, you will see a value like this: \\.\PhysicalDrive5 (Disk5) (Bus: 0, Target: 1, Mon: 0).
Which allows you to know:
- the number of this disk visible to Windows (in this case: number 5)
- its location (in this case: Bus: 0, Target: 1, Mon: 0)

3. Locate a RAID logical drive created on an Adaptec SmartRAID controller on Windows
In Windows, in File Explorer, right-click "Manage" on "This PC" and go to Device Manager.
In the "Disk Drives" section, you will see the RAID logical drives on your Microsemi Adaptec SmartRAID controller listed as "MSCC LOGICAL VOLUME SCSI Disk Device".
If you only have one RAID logical drive, you know this is the one.
However, if you have several RAID logical drives, they will all appear with the same name.

To differentiate them, you need to double click on a disk "MSCC LOGICAL VOLUME..." and look at its location.
In our case: Bus Number 0, Target Id 1, LUN 0.

In the "Volumes" tab you will see the disk number in Windows (Disk 5) which was also visible in maxView Storage Manager (Disk Name: \\.\PhysicalDrive5 (Disk5)).
To see the partitions currently created on this RAID logical drive, click: Populate.

If you go to Windows Disk Management, you can use the disk number displayed by Windows as a basis.
In our case, it is disk 5.
Indeed, the disk name displayed by maxView Storage Manager was "\\.\PhysicalDrive5 (Disk5) (Bus: 0, Target: 1, Mon: 0)".

Otherwise, you can also right-click "Properties" on each disk to find out which disk it is.

As you can see, our disk 5 corresponds to an "MSCC LOGICAL VOLUME SCSI Disk Device" disk.
Again, the location is "Bus Number 0, Target Id 1, LUN 0".

In the "Volumes" tab, you will find the number of this disk, as well as the partitions (volumes) present on it (if applicable).

Share this tutorial
To see also
-

RAID 4/20/2022
Adaptec maxView Storage Manager v3 - Create a RAID volume
-

RAID 4/8/2022
Adaptec maxView Storage Manager v3 - Download and boot on USB version
-

RAID 4/13/2022
Adaptec maxView Storage Manager v3 - Installation on Linux
-

RAID 4/15/2022
Adaptec maxView Storage Manager v3 - Manage an Adaptec SmartRAID controller on VMware ESXi 6.7

You must be logged in to post a comment