- VMware
- VMware vCenter Server (VCSA), VMware vSphere
- 12 February 2025 at 14:30 UTC
-

- 1/2
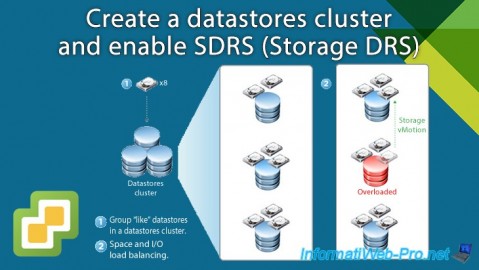
Starting with VMware vSphere 5.0, you can create datastore clusters and enable Storage DRS (SDRS) to optimize your storage management and performance.
- What is Storage DRS (SDRS)?
- Storage DRS (SDRS) features
- Best practices for using Storage DRS (SDRS)
- Create iSCSI disks for datastores
- Configure the software iSCSI controller on your VMware ESXi hosts
- Create VMFS datastores on iSCSI disks
- Create a datastore cluster (Storage DRS POD)
1. What is Storage DRS (SDRS)?
Storage DRS (SDRS) allows you to automatically manage the placement of the virtual disks of your virtual machines when they are created, but also the migration of these to more suitable storage in the future (if necessary).
Indeed, storage DRS (SDRS) allows:
- to manage the space used on your different datastores to prevent one database from being saturated while another is empty.
- to balance inputs/outputs between your different datastores to improve the performance of your virtual machines.
Source : Activate and Deactivate Storage DRS - VMware Docs.
2. Storage DRS (SDRS) features
The features of Storage DRS (SDRS) are:
- resource aggregation: allows you to group together several data banks of the same type (VMFS or NFS) and created on physical storage with equivalent performance.
This grouping of datastores is called a datastore cluster (Storage DRS POD). - initial placement: SDRS will choose the best location for disks when creating a virtual machine, adding a disk, cloning a virtual machine, as well as when you migrate it.
- load balancing based on space and input/output (I/O): by default, SDRS manages the storage of the different disks so as not to exceed 80% usage per data bank and not to exceed the sole 15 ms latency for input/output (I/O).
- maintenance of a datastore: when you need to perform maintenance on a datastore, SDRS is able to migrate the virtual machine storage located there (via Storage vMotion) to other datastores in the cluster to free it.
- inter/intra VM affinity rules: allows you to specify to SDRS whether all the hard disks of the same virtual machine must be stored in the same place or not.
This also allows you to specify whether certain virtual machines should always be stored in the same location or not. This makes it possible, for example, not to store 2 I/O-intensive virtual machines in the same database to avoid saturating the I/O bandwidth of the physical storage.
Note that although SDRS attempts not to exceed 80% disk space usage on your datastores, it is possible for it to exceed this threshold if it is reached on all datastores in the store cluster of data concerned.
In addition, this can also happen depending on the affinity rules you have defined.
Warning : although Storage DRS can be enabled on VMFS or NFS datastore clusters, you cannot mix a VMFS datastore with an NFS datastore in the same datastore cluster.
Source : Storage DRS FAQ (2149938).
3. Best practices for using Storage DRS (SDRS)
When you want to use Storage DRS (SDRS), here is what VMware recommends:
- group disks with similar characteristics. Ex: a RAID 1 volume with a RAID 1 volume, a RAID 5 with a RAID 5, etc.
- It is best if all hosts in a cluster can see all datastores in the datastore cluster.
This improves the performance of Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) and Storage DRS (SDRS). - Do not mix I/O from a non-virtualized workload, from a virtualized workload.
- group datastores created on disks with similar latency. Ex: SSDs (10-15 ms), SAS/FiberChannel disks (20-40 ms) or SATA hard disks (30-50 ms).
In other words, group SSDs in the same cluster or hard drives in the same cluster.
But don't mix SSDs with SATA hard drives in the same datastore cluster.
To learn more about Storage DRS (SDRS), refer to the VMware KB "Storage DRS FAQ (2149938)" which is very comprehensive.
4. Create iSCSI disks for datastores
As noted above, it is recommended that all of your hosts be able to see all of your datastores.
We will therefore use databanks which will be created on iSCSI disks.
For this tutorial, we installed an iSCSI server on Windows Server and we created 2 iSCSI disks of 500 GB each.

5. Configure the software iSCSI controller on your VMware ESXi hosts
For your hosts to have access to your iSCSI disks, you need to select your hosts and go to "Configure -> Storage -> Storage Adapters".
Then follow steps 3 and 4 of our tutorial: VMware vSphere 6.7 - Create an iSCSI datastore.
Once the software iSCSI controller of your VMware ESXi hosts is configured, your iSCSI disks should appear in the "Devices" tab (at the bottom of the page).


6. Create VMFS datastores on iSCSI disks
As explained in steps 5 and 6 of the tutorial cited above, you must select the desired data center and click: Actions -> Storage -> New Datastore.

In the "New Datastore" wizard that appears, select "VMFS" and click Next.

Enter a name for your 1st datastore. For example: iSCSI DS 1.
Then, select the 1st iSCSI disk displayed and click Next (including for the following steps).
Note: host selection does not matter here since the iSCSI disks are visible to both of your hosts.

A summary of your VMFS datastore configuration appears.
Click Finish.

Create a 2nd VMFS datastore.

Specify "iSCSI DS 2" as the name for this datastore and select your 2nd iSCSI disk.

A summary appears.
Click Finish.

Your datastore have been created.

If you select the VMware ESXi host from which you created your datastores and go to "Configure -> Storage -> Storage Adapters -> iSCSI Software Adapter", you will see that the created datastores are displayed .

On the other hand, if you go to the same place for your 2nd VMware ESXi host which sees the same iSCSI disks, you will see that the VMware vSphere Client tells you that these disks are "Not consumed".
It therefore does not automatically see the databanks created on these iSCSI disks.
To fix the problem, simply select the "iSCSI Software Adapter" and click "Rescan Storage".

Leave the 2 boxes to detect in particular the new VMFS volumes created on your iSCSI disks and click OK.

Wait 30 seconds, then click "Refresh" (in the "Devices" tab) if necessary.
As you can see, your 2nd host now sees your new datastores.

Share this tutorial
To see also
-

VMware 6/3/2022
VMware ESXi 7.0 / 6.7 - Install VMware ESXi on an USB key
-
VMware 6/13/2024
VMware vSphere 6.7 - Configure Virtual Flash (SSD cache)
-

VMware 7/19/2024
VMware vSphere 6.7 - Configure your virtual machines settings
-
VMware 11/15/2024
VMware vSphere 6.7 - Migrate VMs via vMotion (rename VM files)

You must be logged in to post a comment