- Firewall
- pfSense
- 23 May 2025 at 11:24 UTC
-

- 1/2
pfSense is software to transform any PC or server into an intelligent network device.
Which means that it has one or more network interfaces (physical, virtual and logical) depending on the needs and services used.
- Network interfaces on pfSense
- List of network interfaces displayed on the dashboard
- Assign interfaces on pfSense
- Interface groups
- Wireless interfaces (Wi-Fi)
- Other types of interfaces
- Configure the WAN interface (connected to the Internet)
- Configure the LAN interface (connected to the local network)
- Switches
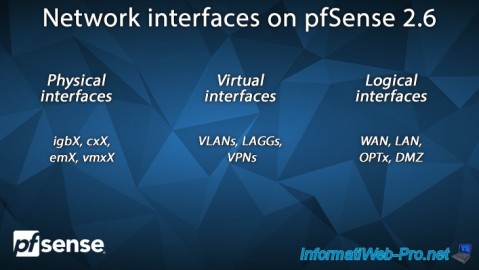
1. Network interfaces on pfSense
1.1. Physical interfaces
Physical interfaces correspond to the network cards or more precisely the physical network ports of the computer or server where pfSense is installed.
The name of these physical interfaces depends on the driver used for them and can therefore be: igbX, cxX, emX, ...
If you virtualize pfSense on VMware Workstation Pro, these physical interfaces will be named: vmx0, vmx1, ...
Source : Assign Interfaces | pfSense Documentation.
1.2. Virtual interfaces
Virtual interfaces are created when you use certain features or services and are therefore linked to them.
For example: VLANs, network link aggregation (LAGG), VPN tunnels, etc.
Source : Interface Types and Configuration | pfSense Documentation.
1.3. Interfaces logiques
Logical interfaces are those that you can configure, such as "WAN" and "LAN" in most cases.
If you purchase a physical appliance (where pfSense is installed), you may have an additional "OPT" port, or even several additional ports: OPT1, OPT2, ...
Common interfaces are:
- WAN: the interface connected to the Internet (directly via PPPoe or PPTP) or indirectly via an intermediate router.
- LAN: the interface connected to the local network where your computers are located.
- OPT: one or more optional interfaces present on certain appliances sold by Netgate (as explained above) and which can be used as you wish (a second WAN, LAN interface, a DMZ, ...).
You will also get OPT interfaces when creating VLANs, ... - DMZ: demilitarized zone allowing you to make servers accessible from the outside while isolating them from the LAN. Thus, if a DMZ server is compromised, machines located on the LAN cannot be attacked via this compromised server.
Sources :
- Netgate Security Gateway Manuals | Netgate Documentation
- Interface Naming Terminology | pfSense Documentation
2. List of network interfaces displayed on the dashboard
On the pfSense dashboard, you will find an "Interfaces" widget listing the interfaces available in your case.
Generally, you will find:
- the WAN interface: interface connected to the Internet.
- the LAN interface: interface connected to the local network.
You will also see the IP address(es) (IPv4 / IPv6) assigned to these network interfaces.
To choose which interfaces should be displayed or not in this widget, click on the small key (framed in red in the image below).

The list of available interfaces appears.
Once the desired interfaces are checked, click Save.

3. Assign interfaces on pfSense
To assign network interfaces on pfSense, go to: Interfaces -> Assignments.

As you can see, on pfSense you can assign logical interfaces (located in the "Interface" column) to physical or virtual interfaces (located in the "Network port" column).
Logical interfaces must therefore be assigned to network ports.
Note that the VLANs will also appear in the "Network port" column (as you can check on the pfSense doc.: Web interface VLAN configuration).
Note that, by default, wireless network interfaces do not appear here.
Indeed, as indicated in the blue box, you must first create wireless network interfaces in the "Wireless" tab before you can associate them with a logical interface here.
Note that a logical interface can only be associated with a network port (and vice versa).

In our case, we have the choice between our 2 physical interfaces (vmx0 and vmx1).

4. Interface groups
On pfSense, you can create interface groups in the "Interface Groups" tab. Which allows you to apply firewall rules or NAT rules across a set of interfaces.
To create a new interface group, click "Add".
Note that an interface group is not an interface type.
Source : Interface Groups | pfSense Documentation.

To create an interface group, specify:
- Group Name: the name of the interface group under which it will appear on pfSense.
- Group Description: a description for this interface group (optional).
- Group Members: interfaces to add to this group.
Then, click Save.

The created interface group appears.

5. Wireless interfaces (Wi-Fi)
To use a wireless interface (Wi-Fi) with pfSense, you will first need to go to the "Wireless" tab and click Add.

Indeed, as indicated in the "Interfaces Assignments" tab, wireless interfaces must first be created via the "Wireless" tab before they can be assigned to a logical interface.

To create a new wireless interface:
- Parent Interface: select the physical interface corresponding to the wireless network card of your pfSense machine.
In our case, we don't have one, so it just says "None available". - Mode: select the desired mode. The available modes are: Infrastructure (BBS), Ad-hoc (IBSS) and Access Point.
- Description: provide a description for this new wireless interface.

Share this tutorial
To see also
-

Firewall 6/25/2025
pfSense 2.6 - 1:1 NAT (IP address mapping)
-

Firewall 5/17/2025
pfSense 2.6 - Enable SSH protocol
-

Firewall 8/20/2025
pfSense 2.6 - Monitoring via SNMPv3 and Zabbix 6
-

Firewall 7/23/2025
pfSense 2.6 - Synchronize the clock from a time server (NTP)

You must be logged in to post a comment