- Windows Server
- 18 June 2021 at 12:27 UTC
-

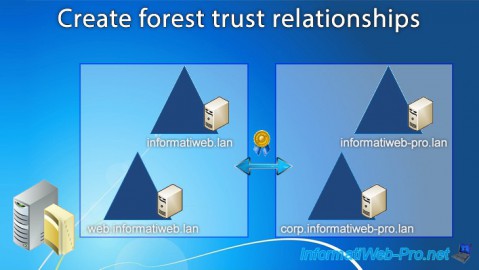
When 2 companies merge (following a buyout or acquisition), it's interesting to create a trust relationship between the forests of these 2 companies (the forest of each company) in order to be able to easily access the resources of the destination forest from the source forest (and vice versa, if desired).
However, before creating this trust relationship, check out our "The basics of Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS)" article to understand how trust relationships work.
- DNS prerequisites
- Create the forest trust relationship
- Forest trust properties
- Connection test on a client PC from the remote forest
- Remove a trust
1. DNS prerequisites
Before you can create a "Forest" type trust relationship between 2 forests, you must ensure that the computers and servers in the source forest can resolve domain names in the remote forest (and vice versa).
In our case, we have 2 forests :
- informatiweb.lan
- informatiweb-pro.lan
The source forest will be "informatiweb.lan" and the remote forest will be "informatiweb-pro.lan".


In order for your Active Directory domain names to be resolvable from one Active Directory forest to another, one of the allowed methods is the use of conditional forwarders on the root domains DNS server.
On the DNS server of the root domain (in our case : informatiweb.lan) of the source forest, open the DNS manager and go to the "Conditional forwarders" folder.
Then, right click in the right part and click on : New Conditional Forwarder.

Specify :
- the root domain name of the remote forest : informatiweb-pro.lan
- the IP address of the master server for this DNS zone.
In our case, the "DC-PRO" domain controller is the server where the DNS server managing the "informatiweb-pro.lan" zone is located and its IP address is : 10.0.0.21
Warning : specify the IP address of the DNS server configured as master DNS server and not a secondary DNS server (which is therefore not authoritative for the desired zone).

We can now resolve domain names that are part of the root domain "informatiweb-pro.lan" thanks to the DNS server where our DNS zone "informatiweb.lan" is located.
When clients attempt to resolve the "xxxxx.informatiweb-pro.lan" domain names, our DNS server will redirect the DNS request to the master DNS server managing the "informatiweb-pro.lan" DNS zone.

Do the same thing in the remote forest to resolve the "xxxxx.informatiweb.lan" domains from the DNS server managing the "informatiweb-pro.lan" DNS zone.
Right click : New Conditional Forwarder.

Specify the root domain name of the source forest (informatiweb.lan) and the IP address of the primary DNS server managing this DNS zone (informatiweb.lan).

There you have it, conditional forwarders are configured on our 2 DNS servers.

2. Create the forest trust relationship
To create a forest trust relationship, preferably go to the domain controller managing the root domain of the source forest (in our case : informatiweb.lan) and launch the "Active Directory Domains and Trusts" console.
Then, right click "Properties" on the root domain (informatiweb.lan) displayed.

In the "Trusts" tab, click on the "New trust" button.

The New Trust Wizard appears.

Specify the root domain name of the remote forest with which you want to create a "Forest" type trust relationship.

Since the source domain and the specified domain are root domains, the wizard asks if you want to create :
- an external trust : an trust only between these 2 root domains. Trust that is not transitive.
- a forest trust : a trust between the 2 forests concerned by the 2 specified root domains (the one you are on and the one you just indicated in the previous step)
In this case, we're going to create a forest trust.

The wizard asks you in which direction(s) you want to create this trust :
- Two-way : in both directions
- One-way - incoming : users from the source forest (in our case : informatiweb.lan) can be authenticated in the destination forest (in our case : informatiweb-pro.lan)
- One-way - outgoing : users of the destination forest (in our case : informatiweb-pro.lan) can be authenticated in the source forest (in our case : informatiweb.lan)

In order for a trust relationship to be used between 2 forests, the trust must be created in the source forest and the destination forest.
The easiest way is to select the "Both this domain and the specified domain" option if you know the credentials of an account allowed to create trust relationships in the remote forest.

If you have chosen the "Both this domain and the specified domain" option, the wizard will ask you for the account credentials to use in the remote forest to create the trust relationship between your 2 forests.

When you create a trust relationship between 2 forests, the wizard offers you to choose between :
- Forest-wide authentication : which allows users to be able to authenticate for all the resources available in the local forest (source forest) from the specified forest (destination forest)
- Selective authentication : limit access to resources in your local forest (source forest)

Then, the wizard will ask you the same question, but for the opposite direction.

A summary of the configuration of your forest trusts is displayed.
Click Next to create them.

After creating the forest trust relationships, click Next again.

Confirm the outgoing and/or incoming trust for this forest trust relationship to be used.


The trust relationship between your 2 forests (in our case "informatiweb.lan" and "informatiweb-pro.lan") has been created.

If you return to the "Trusts" tab of the properties of your source root domain, you will see that an outgoing trust and an incoming trust have been created with the remote forest.
Note that the trust relationship created is of type transitive. It's therefore important to know what this implies for the security of your AD infrastructure.

3. Forest trust properties
To view the properties of these trust relationships, select the desired one and click : Properties.

The properties of your forest trust appear with :
- the root domain of the local forest : informatiweb.lan
- the root domain of the remote forest : informatiweb-pro.lan
- a box indicating whether the remote domain supports Kerberos AES encryption or not
- direction of approval : two-way (in this case)
- information indicating that this trust is transitive in the forest
- a "Validate" button to confirm this trust (if you have not already done so previously when creating it)

In the "Name Suffix Routing" tab, you will see that the routing for name suffixes available in the remote forest is enabled by default.

Finally, you can at any time restrict or not the authentication for all the resources of the remote forest if you wish.

4. Connection test on a client PC from the remote forest
We are creating a new user on our remote forest.

Then, we connect to a client PC linked to our local domain "informatiweb.lan" with the account that we have just created in the remote forest "informatiweb-pro.lan".
As you can see, this works, because the trust relationship between our 2 forests is two-way and therefore allows users from one forest to authenticate in the other forest.

5. Remove a trust
To remove a forests trust, select the outgoing and/or incoming trust, then click : Remove.
In our case, we had created a two-way trust.
So, we select the outgoing approval and we click on Remove.

Select "Yes, remove trust from local domain and other domain" and provide the credentials of an account with administrative rights in the remote forest.

Confirm the deletion of this outgoing trust.

Once the outgoing trust is removed, select the corresponding incoming trust and click "Remove".
Specify the credentials of an account that can administer the remote forest.

Confirm the removal of the incoming trust.

Trusts are removed.

Share this tutorial
To see also
-

Windows Server 4/16/2021
Windows Server - AD DS - How Active Directory replication works
-

Windows Server 4/30/2021
Windows Server - AD DS - Overview of Active Directory functional levels
-
Windows Server 4/3/2021
Windows Server - AD DS - The basics of Active Directory
-

Windows Server 5/21/2021
WS 2016 - AD DS - Add a domain controller to an existing AD domain

You must be logged in to post a comment