By default, all Windows computers and servers running Windows Server use the NETBIOS protocol and can discover the machines on the network (if network discovery is enabled on the client machine) through the broadcast system.
The big problem of the broadcast is that it can consume a lot of bandwidth if a lot of computers use it at the same time. This is likely to be the case in schools and large companies where there are often tens or even hundreds of computers.
To minimize the broadcast, corporate networks and school networks are often subnetted.
But, for the broadcast related to the use of the NETBIOS protocol, this one can be eliminated by using a WINS server.
- Required configuration
- Install a WINS server
- Configure clients to use the WINS server
- Test the WINS server
1. Required configuration
In order for your clients to find your WINS server on the network, you will need to configure 2 DHCP options.
So, you need a DHCP server to use a WINS server in your network.
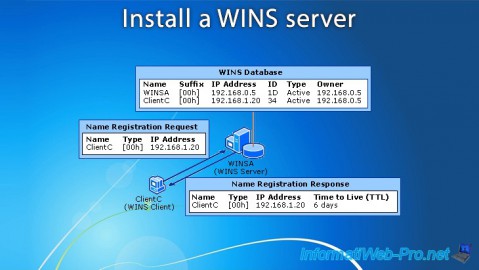
2. Install a WINS server
To install a WINS server, open the Server Manager and click "Add Roles and Features".
Then, select "Role-based or feature-based installation", select your server and click Next.
You arrive at the step regarding server roles. Click Next.

In the features list, check the "WINS-Server" box.

Click Install.

Once installed, click Close.

On the Home screen, you will find the shortcut to open the WINS console.

The WINS console appears.

The "Active Registrations" section displays the workstations that have contacted your WINS server, as well as other types of records.

3. Configure clients to use the WINS server
To let your clients know the IP address of your WINS server, you will need to configure options 44 and 46 of your Microsoft DHCP server.
For this, you have 2 possibilities :
- specify the WINS server address when creating your DHCP scope
- configure options 44 and 46 of the DHCP scope that you had previously created
3.1. Specify the WINS server address when creating a DHCP scope
When you create a new DHCP scope on Windows Server 2012, the wizard will ask you for the address of a WINS server.
At this step, just enter the IP address of your WINS server and click Add.

Then, continue to create your DHCP scope normally.

3.2. Configure options 44 and 46 of a previously created DHCP scope
If you had already created your DHCP scope before, select it and go to "Scope Options".
As you can see, in our case, options 44 and 46 are already present because we specified the WINS server address when creating our DHCP scope.

To configure them manually, right-click on the "Scope Options" item and click on "Configure Options".

Check the "044 WINS/NBNS Servers" box, enter the IP address of your WINS server, and click Add.

Then, check also the "046 WINS/NBT Node Type" box and enter the "0x8" value.

As described in the description of this DHCP option, 0x8 = H (hybrid) node.
Without going into details, using a hybrid node tells Windows to use :
- a P node (0x2) : to allow the computer to register with your WINS server when it starts
- if the WINS server is unreachable, Windows will use a B node (0x1). In other words, it will use the broadcast system it used when there was no WINS server on the network.
In short, the hybrid node allows you to use the WINS server as long as it works and broadcast when the WINS server has a problem.

4. Test the WINS server
To test your WINS server, go to a computer on the network and type these commands at a command prompt :
Batch
ipconfig /release ipconfig /renew
This will force your computer to free the IP address that it currently has (release) and ask for a new one (renew) from your DHCP server.
Thus, it will also receive new DHCP information, including the address of your WINS server.
Then, in the details of your network connection, you will see that the WINS IPv4 server is indicated there.

Now, on your WINS server, go to the "Action -> Show records" menu of the WINS console.

If you leave the default options and click "Search", the WINS server will show you everything it knows.


To view only workstations, go to the "Record Types" tab and click "Clear All".
Then, check only the "WorkStation" box and click on "Find Now".

Now, the WINS console only shows the list of computers that it knows, as well as the name of the workgroup.

Share this tutorial
To see also
-

Windows Server 4/30/2021
Windows Server - AD DS - Overview of Active Directory functional levels
-

Windows Server 12/27/2019
WS 2012 / 2012 R2 - RDS - VDI - Create a virtual desktop infrastructure (pooled virtual desktops)
-

Windows Server 4/19/2019
WS 2012 / 2012 R2 / 2016 - RDS - Unblock your users session as admin
-

Windows Server 7/26/2019
WS 2012 R2 - How the dynamic witness of failover cluster works

You must be logged in to post a comment